So far, the malaria parasite has had a solution to each technique of management we now have thrown at it.
Despite vital advances within the combat against it – together with a vaccine roll-out that held promise, however solely reveals about 30 per cent effectiveness against extreme illness – and dozens of medicine – the parasite all the time makes a comeback.
Currently, the really helpful therapy for malaria an infection is an artemisinin mixture remedy, a mixture of quick and slower-acting medicine designed to deal with malaria an infection and forestall transmission.

However, mixture therapies fail to remedy infections in additional than 50 per cent of sufferers in some Southeast Asian areas. Furthermore, resistance to artemisinins has additionally now been detected in Africa, the place a lot of the 600,000 deaths a yr brought on by malaria happen.
To assist save lives and enhance high quality of life, breakthrough medicine that hit new targets and use new mechanisms of motion are desperately wanted.

Using chemotherapy to combat malaria
Read extra
Professor Leann Tilley, from the Department of Biochemistry and Pharmacology, is a part of a global analysis group working to deal with international considerations that present antimalarial therapies are quickly dropping their effectiveness.
Professor Tilley and colleagues have revealed a world-first discovery within the journal Science displaying {that a} beforehand missed class of chemical compounds – referred to as nucleoside sulfamates or “nukes” – may cause malaria parasite enzymes concerned in protein synthesis to self-destruct.
These new targets are very efficient as a result of protein synthesis enzymes play vital roles within the upkeep and development of cells.
Of explicit significance, inhibitors of this pathway are anticipated to be energetic against all phases of the malaria parasite – efficient for each therapy and stopping transmission to new victims.
Specifically, the nucleoside sulfamates have been discovered to hijack the parasite’s personal cell equipment, inducing enzymes concerned in protein manufacturing to create their very own inhibitors – thereby halting processes which can be important for the parasite’s survival.
This mechanism had not been beforehand reported for protein synthesis enzymes.
“In short, we discovered a new avenue for targeting pathogens – getting them to be the instrument of their own demise,” says Professor Tilley. “The prevention of transmission is very exciting as this will help slow the development of resistance.”
Going international
Working with the height physique for antimalarial drug growth, Medicines for Malaria Venture and Takeda Pharmaceuticals, in addition to analysis labs from throughout 5 continents, the massive worldwide group started their analysis with compounds that Takeda was investigating to deal with most cancers.

Killing the malaria parasite by blocking its recycling system
Read extra
The group recognized a sequence of compounds that have an effect on the malaria parasite however not human cells – however the mechanism of toxicity was not understood.
“We were fortunate to have access to the suite of biochemical and structural biology platforms at the University of Melbourne’s Bio21 Institute of Molecular Science and Biotechnology, as well as The Australian Synchrotron,” says Professor Michael Parker, Bio21 director.
“That allowed us to mount a multi-pronged investigation of the mechanism of action.”
Further work by Dr Stanley Xie and Dr Elyse Dunn, from the Department of Biochemistry and Pharmacology, working carefully with colleagues from Takeda Pharmaceuticals, allowed the group to find that nucleoside sulfamates hijack protein synthesis enzymes to type covalent inhibitor-amino acid conjugates – a bit like super-gluing a key right into a lock in order that the lock not features.
“Excitingly, we discovered a particular compound, ML901, in the Takeda compound library that targets a single plasmodium enzyme and was non-toxic to mammalian cells,” says Professor Tilley.
Colleagues from the Department of Biochemistry and Pharmacology, Dr Riley Metcalf, Dr Craig Morton and Associate Professor Mike Griffin solved the protein’s construction.
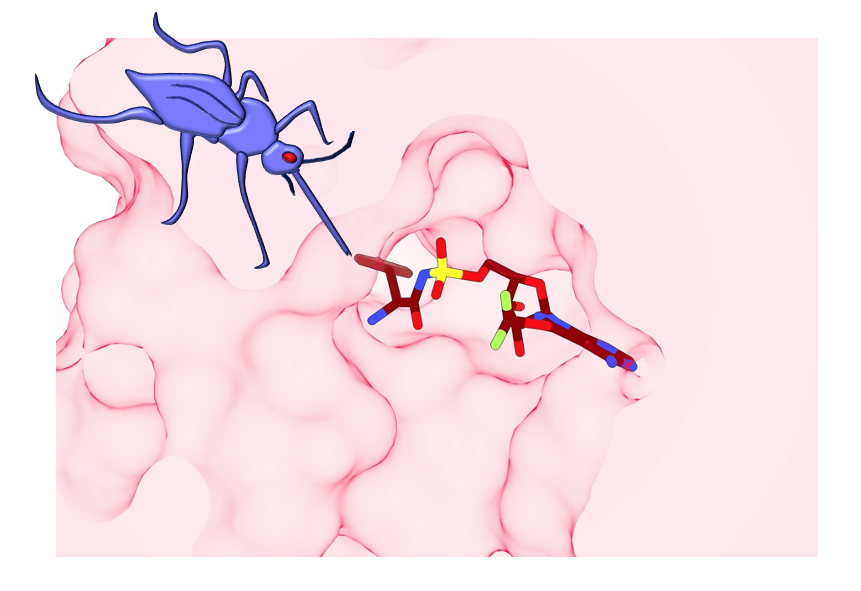
“We discovered a flap of protein that sits over the site where the inhibitor-conjugate binds,” explains Associate Professor Griffin. “The flap appears to hold the working enzyme in an intermediate state that is poised for attack by ML901.

Immunity to COVID-19: Lessons from malaria
Read more
“The human enzyme has a much more open active site, which means it is less susceptible to reaction hijacking by ML901. Our 3D views of the active site were very important to understand why ML901 is so potent and selective.”
The subsequent section was to check ML901 in a set of malaria assays supplied by the Medicines for Malaria Venture. These assays are designed to make sure that drug candidates meet the factors for additional growth.
The group confirmed that ML901 is energetic against all phases and strains of the malaria parasite examined. Importantly, ML901 reveals fast and extended exercise that offers potent parasite killing in an animal mannequin of human malaria assembly the factors for quick and efficient therapy of malaria sufferers.
“The team is now ready to pursue the development of ML901 as a new antimalarial drug candidate,” says Professor Tilley.
New drug discovery avenues await
With at the least 200 million new malaria infections recognized every year, it’s hoped this class of nucleoside sulfamates can have related success to different nucleoside sulfamates that focus on a distinct class of enzymes known as ubiquitin activating (E1) enzymes.
These compounds have been exploited by Takeda to develop a number of new anti-cancer scientific candidates.

“We believe our work here is just the beginning,” says Dr Larry Dick, an Honorary Fellow within the Department of Biochemistry and Pharmacology, and co-lead writer.
“This opens up several important new drug discovery avenues to help address the deadly impact of malaria and other infectious diseases – particularly in developing nations. It could also be used to target other diseases like cancer, neurodegenerative disease, metabolic syndromes including, diabetes and autoimmune disorders.”
According to Professor Tilley, the subsequent step for the group is to tweak the chemical construction to enhance the drug-like properties to optimise the absorption and distribution of the compound within the physique.
“A particularly exciting part of the work is the ability to work with a large, talented and highly collaborative team, bringing together scientists from academia, the pharmaceutical industry and the not-for-profit sector.”
This analysis is funded by the Global Health Innovative Technology (GHIT) fund. The program has obtained approval from the Medicine for Malaria Venture to enter lead optimisation section and the group will now search funding from GHIT for the subsequent growth section.
Banner: Getty Images
The new weapon against malaria’s drug resistance & More Latest News Update
The new weapon against malaria’s drug resistance & More Live News
All this information that I’ve made and shared for you folks, you’ll prefer it very a lot and in it we hold bringing matters for you folks like each time so that you simply hold getting information data like trending matters and also you It is our purpose to have the ability to get
all types of stories with out going by way of us in order that we are able to attain you the newest and finest information without cost with the intention to transfer forward additional by getting the knowledge of that information along with you. Later on, we are going to proceed
to provide details about extra today world news update forms of newest information by way of posts on our web site so that you simply all the time hold shifting ahead in that information and no matter form of data shall be there, it is going to undoubtedly be conveyed to you folks.
The new weapon against malaria’s drug resistance & More News Today
All this information that I’ve introduced as much as you or would be the most totally different and finest information that you simply individuals are not going to get anyplace, together with the knowledge Trending News, Breaking News, Health News, Science News, Sports News, Entertainment News, Technology News, Business News, World News of this information, you may get different forms of information alongside together with your nation and metropolis. You will be capable to get data associated to, in addition to it is possible for you to to get details about what’s going on round you thru us without cost
with the intention to make your self a educated by getting full details about your nation and state and details about information. Whatever is being given by way of us, I’ve tried to deliver it to you thru different web sites, which you’ll like
very a lot and if you happen to like all this information, then undoubtedly round you. Along with the folks of India, hold sharing such information essential to your family members, let all of the information affect them they usually can transfer ahead two steps additional.
Credit Goes To News Website – This Original Content Owner News Website . This Is Not My Content So If You Want To Read Original Content You Can Follow Below Links
