To print this text, all you want is to be registered or login on Mondaq.com.
On 28 June 2019, the Monetary Authority of Singapore
(“MAS”) introduced that it’s going to subject as much as 5 digital
banking licenses 1. This was a revolutionary transfer by
the MAS as digital financial institution licenses have been prolonged to
non-financial institution gamers and allowed banks to function in Singapore with
minimal bodily presence. The MAS recognises that the
banking panorama is present process a elementary transformation pushed
by three key forces: (i) pervasive cell web entry; (ii) the
rise of huge information; and (iii) the expansion of platform ecosystems as a
main new enterprise mannequin in finance. Hence, the digital banking
framework was launched to retain Singapore’s place as one
of the main monetary centres in Asia, and to permit for larger
competitors and spur larger innovation in finance.
The MAS hopes that competitors and innovation from
digital banks might be able to higher serve the wants of society and
the financial system within the following methods: (i) financing the expansion of
infrastructure in rising Asia, and more and more of
local weather-resilient, low-carbon investments; (ii) financing progress
enterprises and small-medium enterprises (“SMEs”); (iii)
decreasing prices and enhancing comfort for shoppers; (iv)
serving to folks to plan early and obtain monetary safety in
their later years; and (v) creating good jobs within the finance
sector. 2
The digital banking framework is along with any digital
banks that Singapore banking teams might already set up beneath the
current web-solely banks (“IOB”) framework. Under
the IOB framework launched in 2000,
Singapore-incorporated banking teams can arrange banking
subsidiaries to pursue new enterprise fashions, together with IOBs.
This permits a financial institution to resolve whether or not it desires to interact in such
actions inside the financial institution or via a separate subsidiary.
Singapore-incorporated banks may select to have a
joint-enterprise companion in establishing the subsidiary, as long as the
Singapore-incorporated banking group retains management over the
enterprise. 3
1. What is a digital financial institution and the way does it differ from a
conventional financial institution?
A digital financial institution can provide related companies to conventional banks,
besides that it’s only allowed to function one bodily place of
enterprise. Unlike conventional banks, a digital financial institution won’t have
bodily branches, automated teller
machines (“ATMs”) or money
deposit machines (“CDMs”), and all
banking companies can be completed on-line.
2. Who is allowed to function a digital
financial institution?
Currently, the MAS has awarded 4 digital financial institution licenses
to the next candidates: 4
(a) Digital Full Bank
- A consortium comprising Grab Holding Inc. and Singapore
Telecommunications Ltd. - An entity wholly-owned by Sea Ltd.
(b) Digital Wholesale Bank
- A consortium comprising Greenland Financial Holdings Group Co.
Ltd, Linklogis Hong Kong Ltd, and Beijing Co-operative Equity
Investment Fund Management Co. Ltd. - An entity wholly-owned by Ant Group Co. Ltd.
In contemplating the candidates for digital financial institution
licenses, MAS would have thought of whether or not the
candidates had a powerful worth proposition and revolutionary digital
enterprise mannequin to supply digital banking companies. 5
3. What are the forms of digital financial institution licenses
out there?
There are two forms of digital financial institution licenses beneath the digital
financial institution licensing framework – a digital full financial institution
(“DFB”) license and a digital wholesale
financial institution (“DWB”) license.
What are the important thing variations between DFBs
and DWBs?
The key variations between DFBs and DWBs are the sort
of banking actions which they will perform and the kind of
clients they will provide their services and products to.
Digital Full Bank License 6
|
Digital Wholesale Bank License
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Permissible actions | All banking companies | Only the proposed enterprise(es) outlined in its utility,
though it might subsequently search approval to broaden its enterprise scope 7 |
| Deposit restrictions | No restrictions on deposits |
|
| Other merchandise and choices to clients | All varieties | Businesses and non-retail clients solely, though MAS might
permit choices to retail clients on an distinctive foundation 8 |
Are DFBs allowed to supply the identical companies as
conventional full banks?
A full functioning DFB is allowed to supply the identical
companies as a conventional full financial institution. However, to minimise dangers to
retail depositors, permissible actions of a DFB will
be phased in by way of a two-stage course of. A DFB will first
begin enterprise as a restricted DFB, which is topic to
restrictions on deposits and product choices. A
restricted DFB additionally has a decrease minimal paid-up capital
requirement in comparison with a full functioning DFB. Once a
restricted DFB has met all of the related milestones and
has been assessed to pose no important supervisory issues, it
will progress to a full functioning DFB.
While MAS doesn’t pre-decide a time interval inside
which a restricted DFB should progress to a full
functioning DFB, it usually expects a DFB to be
absolutely functioning inside 3-5 years from graduation of enterprise.
9 A excessive-stage abstract of the phased strategy is ready out
within the following diagram.
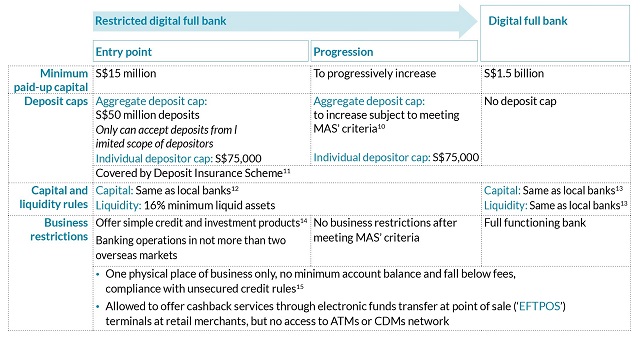
Source:
https://www.mas.gov.sg/-/media/Annex-A-Digital-Full-Bank-Framework.pdf
4. How do you apply for a digital financial institution
license?
Applications for a digital financial institution license should be made to
the MAS throughout the stipulated utility interval. The
first utility interval happened between 29 August 2019 and 31
December 2019. As the Singapore market is comparatively small, solely
4 digital financial institution licenses have been awarded for
now. MAS will proceed to observe market developments and
assessment the necessity to subject extra digital financial institution licences sooner or later.
16
Applicants for the DFB or DWB license should
meet the next necessities 17:
(a) Track report. At least one entity
within the applicant group has 3 or extra years of observe report in
working an current enterprise within the expertise or e-commerce
subject.
(b) Fit and correct standards. The
following individuals are match and correct 18:
- applicant group and their administrators;
- substantial shareholders 19 and 12% controllers
20 of the proposed digital financial institution; and - administrators and government officers 21 of the proposed
digital financial institution, when recognized 22.
( c ) Capital
necessities. Demonstrates the power to fulfill the
relevant minimal paid-up capital requirement on the onset and the
minimal capital funds requirement on an ongoing foundation. This will be
completed by submitting a written affirmation from shareholders of the
proposed digital financial institution on dedication of funds.
(d) Value proposition. Provides clear
worth proposition, incorporating the revolutionary use of expertise
to serve buyer wants and attain beneath-served segments of the
Singapore market.
(e) Sustainable enterprise
mannequin. Demonstrates that the proposed digital
financial institution’s enterprise mannequin is sustainable. The applicant should
present a 5-yr monetary projection of the proposed digital
financial institution, which should present a path in direction of profitability. The assumptions
of the monetary projection should be reviewed by an exterior and
impartial skilled.
(f) Orderly exit plan. Submits a
possible plan that may facilitate the orderly exit of the proposed
digital financial institution.
(g) Commitment from
shareholders. Shareholders of the proposed digital
financial institution decide to offering a letter of accountability and a letter of
endeavor that MAS might require in respect of the
operations of the proposed digital financial institution.
Digital Full Bank License
|
Digital Wholesale Bank License
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Who can apply |
|
|
| Minimum paid-up capital | S$1.5 billion | S$100 million (this is identical as current wholesale
banks) |
5. Are digital banks regulated otherwise from
conventional banks?
Generally talking, DFBs are topic to the identical regulatory
necessities as current full banks, whereas DWBs are topic
to the identical regulatory necessities as current wholesale banks.
These embody necessities referring to expertise dangers,
cash-laundering and terrorism financing dangers, and the conduct of
non-monetary companies.
As an current digital financial institution license holder, what are my
ongoing regulatory necessities?
Banking Act 1970 (“Banking Act”)
(a) Minimum capital necessities
All banks together with digital banks are required to fulfill the
prescribed minimal paid-up capital requirement and minimal capital
funds requirement on an ongoing foundation. Digital banks will even be
topic to the chance-primarily based capital adequacy necessities set out
beneath Notice 637 (Risk Based Capital Adequacy Requirements for
Banks Incorporated in Singapore). 23
(b) Changes in shareholding
Any one that needs to develop into a considerable shareholder, 12%
controller, 20% controller or oblique controller of a licensed
financial institution can be required to acquire prior approval from the
Minister-in-Charge of MAS 24. In specific
for DFB candidates, any in-principal
approvals (“IPA”) granted
by MAS can be on the idea of the shareholding
construction offered to MAS on the utility stage. As
such, if the change within the shareholding now not meets the
eligibility standards for Singaporean management, the IPA might
be revoked.
© Overseas expansions
Pursuant to part 12(3) of the Banking Act, a DWB is
required to acquire MAS’ approval to open a brand new department,
company or workplace in a spot exterior Singapore.
Risk Management
Digital banks ought to confer with MAS’ Framework for Impact
and Risk Assessment of Financial Institutions to higher perceive
how MAS assesses the influence of monetary establishments
25, and the forms of dangers which are usually relevant
to monetary establishments.
(a) Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Countering the Financing
of Terrorism (CFT)
Financial establishments working in Singapore are required to
put in place sturdy controls to detect and deter the movement of
illicit funds via Singapore’s monetary system. Such
controls embody the necessity for monetary establishments to establish
and know their clients (together with useful homeowners), to conduct
common account critiques, and to observe and report any suspicious
transaction. 26
Digital banks can be topic to the identical AML/CFT and
sanctions-associated necessities relevant to the incumbent banks,
together with MAS’ Notice 626 on Prevention of Money
Laundering and Countering the Financing of Terrorism and its
corresponding pointers 27.
(b) Technology Risk
MAS has issued a set of Guidelines on Risk Management
Practices – Technology Risk 28 which units out
expertise danger administration rules and finest practices to information
the monetary establishments to ascertain sound and sturdy expertise
danger governance and oversight, in addition to keep IT and cyber
resilience. MAS has additionally issued Notice 644 (Notice on
Technology Risk Management) 29 on the necessities on
sustaining excessive availability, recoverability, information safety and
incident reporting, and Notice 655 (Notice on Cyber Hygiene)
30 on the important measures that banks should take to
mitigate the rising dangers of cyber threats.
Furthermore, within the wake of current SMS-phishing
scams, MAS and the Association of Banks in
Singapore (“ABS”) are additionally
introducing a set of extra measures to bolster the safety of
digital banking. 31
© Outsourcing Risks
As a digital financial institution might once in a while enter into preparations
with third celebration service suppliers to outsource sure enterprise
and assist features, it is usually required to have in place the
related governance and danger administration processes to establish and
handle the dangers arising from these outsourcing preparations.
Digital banks ought to confer with MAS’ Guidelines on
Outsourcing 32 that units out MAS’ expectations
of a monetary establishment that has entered or is planning to enter
into an association to outsource any of its enterprise features to a
service supplier.
Conduct of non-monetary companies
In September 2017, MAS sought public suggestions on its
proposal to refine its anti-commingling framework for banks in two
key points: (i) to streamline the circumstances and necessities for
banks to conduct or put money into permissible non-monetary companies;
and (ii) to permit banks to interact within the operation of digital
platforms that match consumers and sellers of client items or
companies, in addition to the net sale of such items and companies.
Digital banks ought to, when planning to conduct any non-monetary
companies, contemplate MAS’ Consultation Paper and Response
to Feedback Received on its Review of Anti-Commingling Framework
for Banks 33, which units out MAS’s coverage
in direction of banks’ conduct of non-monetary companies.
Securities and Futures Act
2001 (“SFA”) / Financial
Advisers Act 2001 (“FAA”)
Digital banks will even be anticipated to fulfill the related
regulatory necessities beneath the SFA and
the FAA and submit the related types the place it intends to
perform regulated actions beneath
the SFA 34 or monetary advisory companies
beneath the FAA 35. When submitting the related
kind, the digital financial institution is just not required to resubmit data that
was already offered in its utility to arrange a digital financial institution
(until there have been any modifications to the knowledge beforehand
offered).
6. Regional Developments
Hong Kong
Digital banks are termed as “virtual banks” in Hong
Kong, and outlined as “a financial institution which primarily delivers retail
banking companies via the web or different types of digital
channels as a substitute of bodily branches”. 36 As at 31
December 2021, the Hong Kong Monetary Authority has issued a complete
of 8 digital financial institution licenses. 37
Malaysia
On 2 July 2021, Bank Negara
Malaysia (“BNM”) introduced
that it had acquired 29 purposes for its digital banking
license and is ready to subject as much as 5 digital banking licenses in
early 2022. 38 Similar to Singapore’s strategy
in direction of DFBs, BNM implements a phased strategy
in direction of its digital banking license holders, such {that a} simplified
regulatory framework is utilized throughout its preliminary three to 5
years of operations, to permit the license holders to show
its viability and sound operations, and for BNM to
observe attendant dangers. 39
Indonesia
The Financial Services Authority (Otoritas Jasa
Keuangan) of Indonesia issued new laws in August
2021 to introduce its digital financial institution regulatory framework, which
permits for digital banking to be carried out by means of an
institution of a brand new digital financial institution, or a change of an
current standard financial institution right into a digital financial institution.
Philippines
The Central Bank (Bangko Sentral ng
Pilipinas) of the
Philippines (“BSP”) issued its
Guidelines on the Establishment of Digital Banks in December 2020
for the inclusion of “Digital Banks” as a definite
classification of banks and to set out its corresponding licensing
framework in its current Manual of Regulations for Banks. Similar
to Indonesia, the rules permit for the institution of a brand new
digital financial institution, or the conversion of an current financial institution to a digital
financial institution. 40 However, BSP introduced that as at 1
September 2021, it will cease accepting purposes for digital
banking licenses for 3 years, to permit the authorities to observe
the digital banking trade. The variety of digital banking
licenses issued can be capped at 7. 41
This article has been produced for basic informational
functions solely. The data contained on this article mustn’t
be construed as authorized recommendation and isn’t supposed to be a substitute
for authorized counsel on any material. No recipient of this
article ought to act or chorus from appearing on the idea of any
contents on this article with out in search of applicable authorized or different
skilled recommendation.
Footnotes
1
https://www.mas.gov.sg/news/media-releases/2019/mas-to-issue-up-to-five-digital-bank-licences
2
https://www.mas.gov.sg/news/speeches/2019/banking-liberalisations-next-chapter-digital-banks
3
https://www.mas.gov.sg/-/media/Digital-Bank-Licence/FAQs-on-DFB-and-DWB-Licences.pdf?la=en&hash=6883
4
https://www.mas.gov.sg/news/media-releases/2020/mas-announces-successful-applicants-of-licences-to-operate-new-digital-banks-in-singapore
5
https://www.mas.gov.sg/news/speeches/2019/banking-liberalisations-next-chapter-digital-banks
6 The data on this desk is offered on the
assumption that the DFB is a full
functioning DFB.
7 Generally, the permissible actions for a digital
wholesale financial institution are outlined within the Guidelines for Operation of
Wholesale Banks revealed by the MAS on 31 July
2008.
8 Non-retail clients confer with people who fall
inside the definition of “accredited investor” beneath the
Securities and Futures Act 2001. MAS doesn’t anticipate
a DWB to serve retail clients, comparable to offering
monetary recommendation to those people. On an distinctive
foundation, MAS might permit such choices, offered that there
is a powerful nexus and is critical to the applicant’s core
providing(s) to the non-retail section. An applicant with plans to
present any of such choices ought to spotlight accordingly in its
utility, and clarify how there’s a sturdy nexus and is
essential to the particular core providing(s) to the non-retail
section.
9
https://www.mas.gov.sg/-/media/Digital-Bank-Licence/Eligibility-Criteria-and-Requirements-for-Digital-Banks.pdf?la=en&hash=57410B76A3359791816B0A0BD592DF8EF2D37B33
10 Wholesale deposits won’t be topic to the
combination deposit cap as soon as the restricted full financial institution’s paid-up
capital reaches $100m (according to wholesale financial institution’s minimal
paid-up capital).
11 The Deposit Insurance Scheme will shield non-financial institution
depositors (together with people and sole proprietorships) within the
occasion of a financial institution’s failure by protecting
the SGD deposits positioned with a member financial institution, for as much as
S$75,000 per depositor per member financial institution.
12 6.5% CET1 Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR), 10%
Total CAR, 2.5% capital conservation buffer (CCB), as much as 2.5%
countercyclical capital buffer (CCyB).
13 100% web steady funding ratio, 100% liquidity protection
ratio.
14 Interested events can confer with the Schedule to the
Securities and Futures (Capital Markets Products) Regulations 2018
for potential scope of permissible funding merchandise that may be
supplied.
15 Interested events can confer with MAS Notice
635 Unsecured Credit Facilities to Individuals and Banking (Credit
Card and Charge Card) Regulations 2013 for reference.
16
https://www.mas.gov.sg/-/media/Digital-Bank-Licence/FAQs-on-DFB-and-DWB-Licences.pdf?la=en&hash=6883
17
https://www.mas.gov.sg/-/media/Digital-Bank-Licence/Eligibility-Criteria-and-Requirements-for-Digital-Banks.pdf?la=en&hash=57410B76A3359791816B0A0BD592DF8EF2D37B33
18 See Guidelines on Fit and Proper Criteria.
19 “substantial shareholder” has the identical
that means as in part 81 of the Companies Act. It usually refers
to any one that can have a voting curiosity of a minimum of 5% within the
proposed digital financial institution.
20 “12% controller” means an individual, not being a
20% controller, who alone or collectively together with his
associates:
a holds not lower than 12% of the whole variety of issued
shares within the proposed digital financial institution; or
b) is able to management voting energy of not much less
than 12% within the proposed digital financial institution.
Please confer with part 15B of the Banking
Act.
21 “executive officer”, in relation to a
firm, means any individual, by no matter title described,
who:
a) is within the direct employment of, or appearing for or by
association with, the corporate; and
b) is anxious with or takes half within the administration of
the corporate on a day-to-day foundation.
Please confer with part 2 of the Banking Act.
22 The proposed digital financial institution’s board of administrators and
staff of government officers needn’t be absolutely fashioned at time of
utility.
23
https://www.mas.gov.sg/-/media/MAS/Regulations-and-Financial-Stability/Regulations-Guidance-and-Licensing/Commercial-Banks/Regulations-Guidance-and-Licensing/Notices/MAS-Notice-637-effective-1-January-2022.pdf
24 Sections 15A and 15B of the Banking Act
25
https://www.mas.gov.sg/-/media/MAS/News-and-Publications/Monographs-and-Information-Papers/Monograph—MAS-Framework-for-Impact-and-Risk-Assessment.pdf
26
https://www.mas.gov.sg/regulation/notices/notice-626
27 https://www.mas.gov.sg/regulation/notices/notice-626
and
https://www.mas.gov.sg/regulation/guidelines/guidelines-to-notice-626-on-prevention-of-money-laundering-and-cft-for-banks
28
https://www.mas.gov.sg/-/media/MAS/Regulations-and-Financial-Stability/Regulatory-and-Supervisory-Framework/Risk-Management/TRM-Guidelines-18-January-2021.pdf
29
https://www.mas.gov.sg/-/media/MAS/Notices/PDF/Notice-MAS-644.pdf
30
https://www.mas.gov.sg/-/media/MAS/Notices/PDF/MAS-Notice-655.pdf
31
https://www.mas.gov.sg/news/media-releases/2022/mas-and-abs-announce-measures-to-bolster-the-security-of-digital-banking
32
https://www.mas.gov.sg/-/media/MAS/Regulations-and-Financial-Stability/Regulatory-and-Supervisory-Framework/Risk-Management/Outsourcing-Guidelines_Jul-2016-revised-on-5-Oct-2018.pdf
33
https://www.mas.gov.sg/publications/consultations/2017/consultation-paper-on-review-of-anti-commingling-framework-for-banks
34 Form 26- Notice of Commencement of Business lodged
pursuant to Regulation 14(4) of the Securities and Futures
(Licensing and Conduct of Business) Regulations by individuals exempt
from holding a Capital Markets Services License beneath part
99(1)(a), (b), ( c ) and (d) of the SFA
35) Form 26 – Notice of Commencement of Business
lodged pursuant to Regulation 37(1) of the Financial Advisers
Regulations by individuals exempt from holding a Financial
Adviser’s License beneath Section 23(1)(a), (b), ©, (d) and
(e) of the FAA
36
https://www.hkma.gov.hk/media/eng/doc/key-information/press-release/2018/20180530e3a2.pdf
37
https://www.hkma.gov.hk/eng/key-functions/banking/banking-regulatory-and-supervisory-regime/virtual-banks/
38
https://www.bnm.gov.my/-/bnm-receives-29-applications-for-digital-bank-licenses
39
https://www.bnm.gov.my/documents/20124/938039/20201231_Licensing+Framework+for+Digital+Banks.pdf
40
https://www.bsp.gov.ph/Regulations/Issuances/2020/c1105.pdf
41
https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2021-08-19/philippines-set-to-close-digital-bank-applications-for-3-years
The content material of this text is meant to supply a basic
information to the subject material. Specialist recommendation ought to be sought
about your particular circumstances.
The Evolution Of Banks In Singapore: Things You Need To Know About The Regulation Of Digital Banks – Financial Services & More Latest News Update
The Evolution Of Banks In Singapore: Things You Need To Know About The Regulation Of Digital Banks – Financial Services & More Live News
All this information that I’ve made and shared for you folks, you’ll prefer it very a lot and in it we hold bringing matters for you folks like each time so that you just hold getting information data like trending matters and also you It is our aim to have the ability to get
every kind of reports with out going via us in order that we will attain you the most recent and finest information totally free as a way to transfer forward additional by getting the knowledge of that information along with you. Later on, we are going to proceed
to offer details about extra today world news update forms of newest information via posts on our web site so that you just at all times hold shifting ahead in that information and no matter type of data can be there, it can positively be conveyed to you folks.
The Evolution Of Banks In Singapore: Things You Need To Know About The Regulation Of Digital Banks – Financial Services & More News Today
All this information that I’ve introduced as much as you or would be the most totally different and finest information that you just persons are not going to get wherever, together with the knowledge Trending News, Breaking News, Health News, Science News, Sports News, Entertainment News, Technology News, Business News, World News of this information, you may get different forms of information alongside along with your nation and metropolis. You will be capable to get data associated to, in addition to it is possible for you to to get details about what’s going on round you thru us totally free
as a way to make your self a educated by getting full details about your nation and state and details about information. Whatever is being given via us, I’ve tried to convey it to you thru different web sites, which you’ll like
very a lot and for those who like all this information, then positively round you. Along with the folks of India, hold sharing such information essential to your family members, let all of the information affect them and so they can transfer ahead two steps additional.
Credit Goes To News Website – This Original Content Owner News Website . This Is Not My Content So If You Want To Read Original Content You Can Follow Below Links
