Scientists throughout the world are continually working to develop effective coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines and therapeutics. The emergence of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants, such as the Omicron and Delta variants, have significantly reduced the efficacy of available vaccines.
Study: CD8 T Cells Contribute to Vaccine Protection Against SARS-CoV-2 in Macaques. Image Credit: Dotted Yeti / Shutterstock.com
Background
The effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines is often determined by the level of antibody responses elicited following vaccination. Preclinical and clinical studies have suggested that CD8+ T-cell responses are also associated with natural immune protection against SARS-CoV-2, especially when antibodies provide only partial protection.
Greater durability and cross-reactivity have been reported for cellular immune responses as compared to neutralizing antibody (nAb) responses against SARS-CoV-2 variants. Importantly, both messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) and adenovirus vector-based vaccines are associated with 70% and 85% efficacy, respectively, against the Omicron BA.1 variant in the absence of Omicron-specific nAbs. Thus, other immune responses, aside from nAbs, have an important role in providing protection against severe COVID-19.
Although virus-specific CD8+ T-cells can detect and remove infected cells, their direct function in vaccine protection against COVID-19 has not yet been determined. To date, all Phase III clinical trials of COVID-19 vaccines have excluded the evaluation of cellular immune responses as an immune correlate. In a recent Science Immunology study, scientists evaluate the role of CD8+ T-cells in vaccine protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection in rhesus macaques.
About the study
A total of 30 adult male and female Rhesus macaques were allocated to six experimental groups. All animals were immunized with 5×1010 viral particles of the Johnson & Johnson Ad26.COV2.S adenovirus vector-based vaccine, which is equivalent to a human dose of the vaccine.
All test rhesus macaques were immunized through the intramuscular route at week zero. The test animals were subsequently injected with CD8-depleting monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) at week five, which was followed by the Delta variant challenge at week six.
Each group received 50 mg/kg of the anti-CD8β CDR-grafted rhesus immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) antibody (CD8b255R1), the anti-CD8α CDR-grafted rhesus IgG1 antibody (MT807R1), or an isotype-matched control antibody.
Study findings
Vaccination with Ad26.COV2.S elicited CD8+ T-cells that significantly contributed to controlling SARS-CoV-2 in a high dose heterologous challenge with the Delta variant in rhesus macaques.
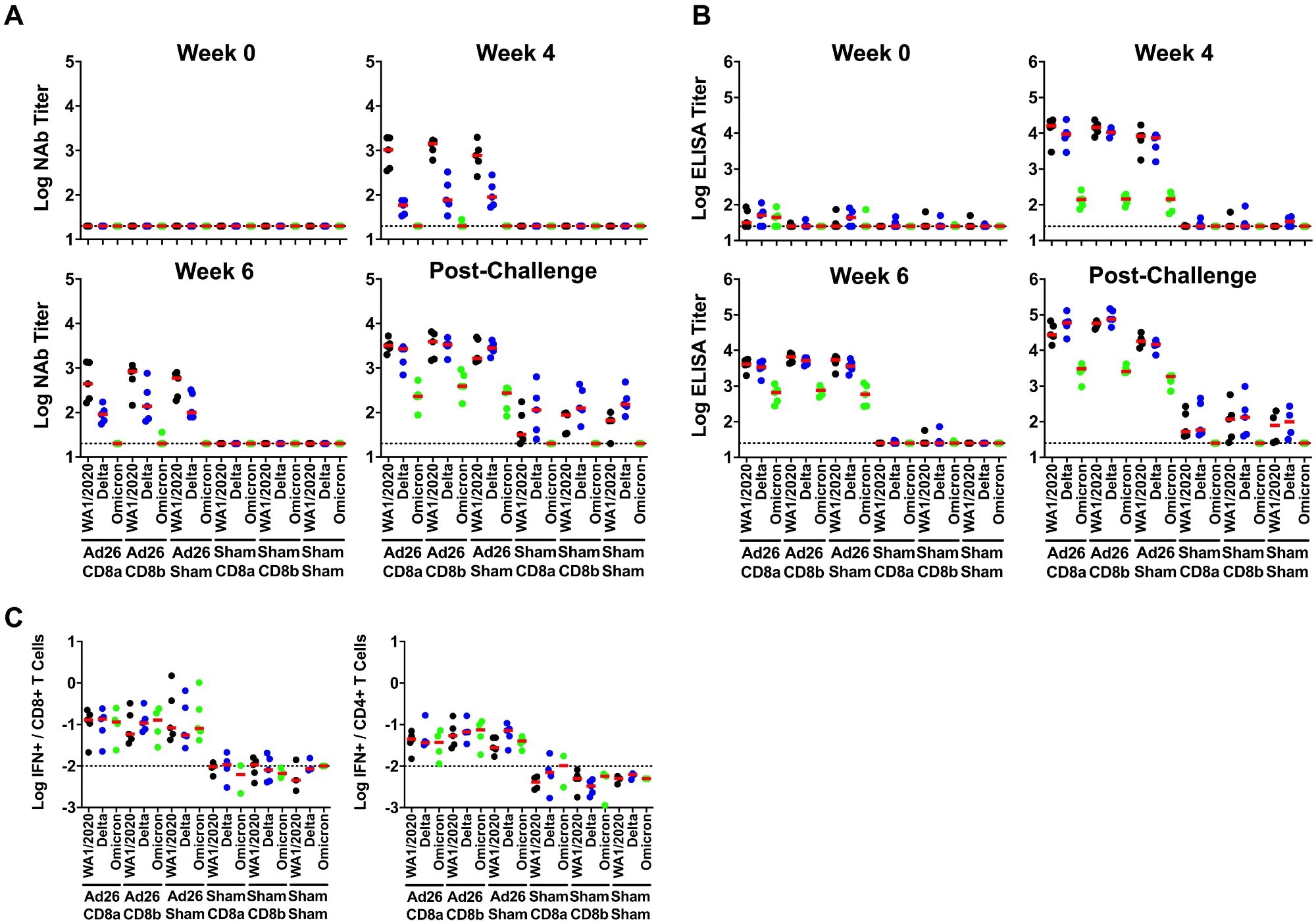
Immune responses following vaccination. Antibody responses at weeks 0, 4, and 6 following vaccination with Ad26.COV2.S and following challenge. A, Neutralizing antibody (NAb) titers by a luciferase-based pseudovirus neutralization assay. B, Receptor binding domain (RBD)-specific binding antibody titers by ELISA. C, Pooled peptide Spike-specific IFN-γ CD8+ and CD4+ T cell responses by intracellular cytokine staining assays at week 2 following vaccination with Ad26.COV2.S. Responses were measured against the SARS-CoV-2 WA1/2020 (black), B.1.617.2 (Delta; blue), and B.1.1.529 (Omicron; green) variants. Dotted lines represent limits of quantitation. Medians (red bars) are shown.
In vaccinated animals, a reduction in CD8+ T-cells caused a higher viral load in the upper and lower respiratory tracts after animals were inoculated with the Delta variant. CD8α depletion had a greater impact on viral loads, perhaps because of the functional role of natural killer (NK) cells or CD8 depletion with the anti-CD8α mAb.
Previous observations that BNT162b2 and Ad26.COV2.S vaccines provided significant protection against severe infection with Omicron BA.1 variant, in the absence of Omicron-specific nAbs, were similarly reported in the current study. Previous studies have also indicated that, unlike nAb responses, T-cell responses exhibit higher cross-reactivity against SARS-CoV-2 variants, including Omicron BA.1, which was also supported in the current study. Thus, these findings establish a definitive immunogenic context for clinical observations.
Ad26.COV2.S vaccination induced CD8+ T-cell responses and contributed to controlling the viral load in rhesus macaques challenged with SARS-CoV-2 in a high-dose heterologous challenge model. The current model only focused on the virologic control in animals challenged with the SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant; thus, this animal model cannot be used to determine the role of CD8+ T-cell responses in providing protection during COVID-19.
A previous macaque model-based study reported that higher antibody titers can prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection. However, all currently available COVID-19 vaccines show modest and brief efficacy in protecting individuals from contracting the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant, even after booster vaccination.
Conclusions
In summary, the present study highlighted the significant contribution of CD8+ T-cell responses following vaccination with Ad26.COV2.S in providing protection against SARS- CoV-2 replication using a rhesus macaques model.
The authors speculated that CD8+ T-cell responses also controlled the viral load after mRNA vaccination; however, this observation requires further experimental validation. Importantly, CD8+ T-cell responses adeptly restrict SARS-CoV-2 variants, such as the Delta and Omicron strains, which have been found to partially evade nAb responses.
In the future, researchers must determine if CD8+ T-cell responses also positively affect SARS-CoV-2 vaccine protection in humans. Thus, further studies should also focus on T-cell responses, along with antibody titers, to evaluate vaccine efficacy in humans.
Journal reference:
- Liu, J., Yu, J., McMahan, K., et al. (2022) CD8 T Cells Contribute to Va ccine Protection Against SARS-CoV-2 in Macaques. Science Immunology. doi:10.1126/sciimmunol.abq7647.
In monkeys, spike-based vaccines produce some immunity based on CD8 T-cells & Latest News Update
In monkeys, spike-based vaccines produce some immunity based on CD8 T-cells & More Live News
All this news that I have made and shared for you people, you will like it very much and in it we keep bringing topics for you people like every time so that you keep getting news information like trending topics and you It is our goal to be able to get
all kinds of news without going through us so that we can reach you the latest and best news for free so that you can move ahead further by getting the information of that news together with you. Later on, we will continue
to give information about more today world news update types of latest news through posts on our website so that you always keep moving forward in that news and whatever kind of information will be there, it will definitely be conveyed to you people.
In monkeys, spike-based vaccines produce some immunity based on CD8 T-cells & More News Today
All this news that I have brought up to you or will be the most different and best news that you people are not going to get anywhere, along with the information Trending News, Breaking News, Health News, Science News, Sports News, Entertainment News, Technology News, Business News, World News of this made available to all of you so that you are always connected with the news, stay ahead in the matter and keep getting today news all types of news for free till today so that you can get the news by getting it. Always take two steps forward
Credit Goes To News Website – This Original Content Owner News Website . This Is Not My Content So If You Want To Read Original Content You Can Follow Below Links
